Unit 5: Social, Cultural and Global Challenges
Diversity of Different Generations in the Workplace
Workplace diversity includes employees from multiple generations, each with distinct values, work styles, and expectations. Today’s workforce typically consists of:
Challenges of a Multi-Generational Workforce
Benefits of Generational Diversity
Solutions for a Cohesive Multi-Generational Workplace
- Promote cross-generational mentoring programs.
- Encourage open communication through diverse platforms.
- Provide flexible work options to meet different needs.
- Offer technology training to bridge the digital divide.
- Foster inclusive leadership that values all age groups.
Issue of Inter-Generational Equity
Inter-generational equity refers to the fair distribution of resources,
opportunities, and responsibilities between different generations. It
ensures that future generations inherit a sustainable world while addressing
the needs of the present generation.
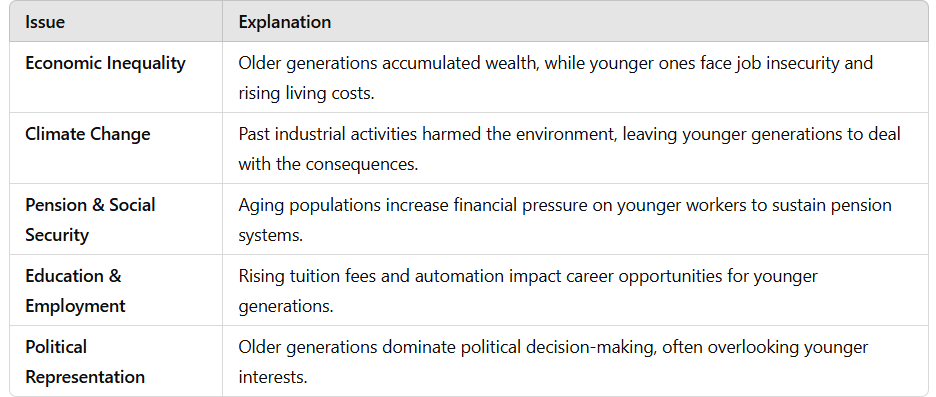
Key Issues
Examples of Inter-Generational Inequity
- Climate Change: Policies made decades ago led to pollution, global warming, and extreme weather, affecting today’s youth.
- Housing Crisis: Rising property prices make homeownership difficult for younger generations.
- Economic Burden: Government debts and pension liabilities fall on younger taxpayers.
Solutions for Inter-Generational Equity
In Short, Inter-generational equity is crucial for a sustainable and fair
society. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to
create policies that ensure prosperity for both present and future
generations.
Migration
Migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another, often
across borders, due to economic opportunities, political instability, or
human rights concerns. It has significant implications from multiple
perspectives:
Political Perspective
Migration is a key political issue, influencing national policies,
international relations, and electoral outcomes.
Economic Perspective
Migration has both positive and negative effects on the economy of both
origin and destination countries.
Human Rights Perspective
Migration raises concerns about human rights, particularly for refugees
and undocumented migrants.
The Migrant Crisis in the EU
The European migrant crisis peaked in 2015–2016, when millions of
refugees and economic migrants arrived in Europe, primarily from the
Middle East, Africa, and South Asia.
Causes of the EU Migrant Crisis
Challenges Faced by the EU
EU’s Response to the Crisis
Current Situation (Post-2020s)
- Migration remains a divisive issue in European politics.
- Some countries continue to tighten asylum laws and increase border security.
- The Ukraine War (2022) caused another wave of refugees into the EU.
- Climate change may lead to more migration in the future.
In Short, Migration is a complex global issue with political,
economic, and humanitarian dimensions. While it presents economic
opportunities and cultural diversity, it also poses significant
challenges in governance, security, and human rights. The EU migrant
crisis highlights the need for a balanced approach that ensures border
security, fair asylum policies, and humanitarian support.
Climate Change
Political Dimensions of Climate Change
Climate change is not just an environmental issue—it has major
political implications. Governments, international organizations, and
corporations engage in climate policies, negotiations, and strategies
that impact economies, national security, and global relations.
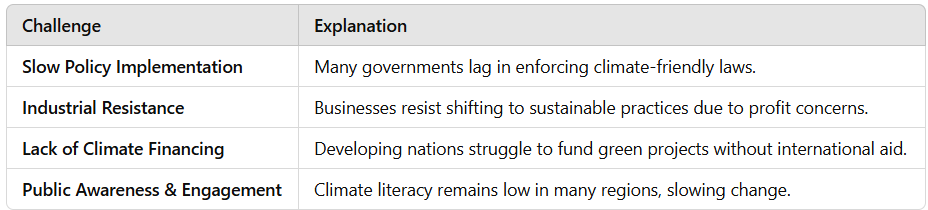
Political Challenges of Climate Change
Major International Climate Agreements
Geo-Political Impacts of Climate Change
- Countries with abundant renewable resources (e.g., solar in the Middle East) gain strategic importance.
- Rising tensions over water resources (e.g., India-Pakistan Indus Water Treaty, Nile River disputes).
- Climate change influences elections and policies (e.g., Green New Deal in the U.S., EU carbon taxes).
Plight and Issues of Climate Refugees
Who are Climate Refugees?
Climate refugees are people forced to leave their homes due to
environmental disasters such as rising sea levels, extreme weather,
droughts, and desertification.
Causes of Climate Migration
Challenges Faced by Climate Refugees
Potential Solutions
- Legal Recognition: UN and countries should amend refugee laws to include climate migrants.
- Resettlement Programs: Governments should develop policies for relocating displaced populations.
- Sustainable Adaptation Strategies: Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Global Cooperation: Developed nations should support climate-affected regions financially and technologically.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Climate Action
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a
global framework to address environmental, social, and economic
challenges.
Key Climate-Related SDGs
Challenges in Achieving Climate SDGs
Strategies to Achieve Climate Goals
- Investment in Green Technologies: Expanding solar, wind, and hydro energy.
- Carbon Pricing & Emission Reductions: Taxing polluters and setting strict emission limits.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Smart cities, electric transport, and green infrastructure.
- Strengthening Global Climate Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, businesses, and NGOs.
In Short, Climate change is a political, economic, and humanitarian
crisis requiring urgent action. Addressing climate refugees and ensuring
sustainable development are crucial for a stable and equitable future.
Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to implement
long-term solutions for climate resilience.
Rising Inequality
Historical Context of Inequality
Inequality has been a persistent issue throughout history, influencing
social structures, political power, and economic systems. It has often led
to revolutions, protests, and policy changes.
Social Unrest Due to Inequality
Global Inequality
Global inequality refers to the uneven distribution of wealth, resources,
and opportunities between countries and within societies. It affects
education, healthcare, employment, and living standards.
Causes of Global Inequality
Effects of Global Inequality
Regions Facing High Inequality
Economic Reforms
In Short, Rising inequality is a major global challenge, linked to
historical power structures, economic policies, and globalization.
Addressing inequality requires strong social and economic reforms, fair
taxation, improved access to education and healthcare, and a commitment
to sustainable development. Without action, growing disparities could
lead to greater social unrest and economic instability worldwide.
Privacy in the Digital World
Digital privacy refers to the protection of personal data and online
activities from unauthorized access, surveillance, and misuse. As
technology advances, concerns about data security, surveillance, and
corporate control over personal information have grown significantly.
Complexity of Privacy Issues
Digital privacy is complex due to multiple factors, including legal,
technological, and ethical challenges.
Key Privacy Issues
Examples of Privacy Breaches
- Cambridge Analytica Scandal (2018): Facebook data was misused for political advertising.
- Google & Amazon Data Tracking: Users' activities are continuously monitored to serve personalized ads.
- Mass Government Surveillance: Programs like the U.S. PRISM program collect global online communications.
Basics of GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a data privacy law
enacted by the European Union (EU) in 2018. It regulates how
businesses and organizations collect, store, and use personal data of
EU citizens.
Key Principles of GDPR
GDPR Fines & Penalties
- Companies violating GDPR can face fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue, whichever is higher.
- Tech giants like Google, Meta, and Amazon have faced hefty GDPR fines for data privacy violations.
Importance of Personal Data
Why Personal Data Matters?
Personal data includes names, addresses, phone numbers, financial
details, browsing history, biometric data, and more. This data is
valuable for both individuals and corporations.
In Short, Privacy in the digital world is complex and evolving due to
increasing data collection and surveillance. GDPR is a major step toward
regulating data protection, but individuals must also take measures to
safeguard their personal information. As technology advances, striking a
balance between convenience, security, and ethical data usage will
remain a crucial challenge.
Existential Threats
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries and daily
life, but it also presents existential threats that could impact
humanity's survival, security, and ethical foundations. These risks
require urgent global attention and the development of new ethical
frameworks.
Five Types of Risks Associated with AI
AI poses multiple risks that can threaten individuals, societies, and
even global stability. The five key existential risks associated with
AI include:
1. Autonomous Weapons & AI in Warfare
2. Superintelligent AI & Loss of Human Control
3. Economic Disruptions & Mass Unemployment
4. Misinformation & AI-Generated Fake Content
5. Bias, Ethics, and Social Control
Need for New Age Ethics in AI
To address these threats, a new ethical framework is needed to govern AI
development, implementation, and impact.
Key Ethical Principles for AI
Solutions for Ethical AI Development
- Global AI Regulations: Governments should create international policies on AI safety.
- AI Governance Bodies: Independent organizations should oversee AI development and ensure compliance.
- Ethical AI Research: Scientists must integrate ethics into AI programming.
- Public Awareness & AI Literacy: People must be educated about AI risks and responsible usage.
In Short, AI presents immense potential but also significant existential
risks. Without ethical safeguards, AI could threaten global security,
employment, and personal freedoms. New-age ethics must focus on human
oversight, fairness, accountability, and long-term AI safety to ensure AI
benefits society without causing irreversible harm.