Unit II: Market communication
Market Communication
Market communication refers to the strategies and tools used by businesses to convey messages to their target audience, build brand awareness, and influence consumer behavior. It includes all forms of communication that help promote a product, service, or brand.
In Other word, Market communication refers to the various methods and strategies that a company uses to convey messages about its products, services, and brand to its target audience. It involves advertising, promotions, public relations, social media, and direct marketing.
Objective
- Inform potential customers about a product or service.
- Persuade customers to make a purchase.
- Build a strong brand image and customer relationships.
Key Elements of Market Communication
- Message: What the company wants to convey.
- Medium: The channel used to deliver the message (TV, social media, print ads, etc.).
- Target Audience: The specific group of customers the message is aimed at.
- Feedback: The response or reaction from the audience.
Example: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign replaced its logo with popular names on bottles. This created a personal connection with customers, leading to increased engagement and sales.
Brand Expression
Brand expression refers to how a brand presents itself across various touchpoints to create a distinct and consistent identity. It includes visual identity, messaging, tone, and customer experience.
In Other Words, Brand expression is the way a company presents itself to the world, including its visual identity, messaging, and customer interactions. It is how a brand communicates its values, personality, and emotions to its audience.
Components of Brand Expression
- Logo and Design: The visual symbols that represent the brand (e.g., Apple’s bitten apple logo).
- Tagline & Messaging: Slogans or phrases that define the brand’s mission (e.g., Nike’s “Just Do It”).
- Brand Voice & Tone: The way a brand communicates (formal, friendly, professional, etc.).
- Customer Experience: How customers feel when they interact with the brand.
Example: Tesla expresses its brand through innovation, minimalistic design, and a futuristic approach. Its communication focuses on sustainability and cutting-edge technology, making it stand out in the electric vehicle industry.
Communication Mix
A communication mix is the combination of various marketing communication tools used to reach and influence the target audience.
Components of the Communication Mix
Example: Nike’s communication mix includes TV commercials featuring athletes (advertising), social media campaigns (digital marketing), sponsorships of sports teams (PR), and limited-time discounts on its website (sales promotion).
Customer Acquisition Process
Steps in Customer Acquisition:
- Awareness: Making customers aware of your brand through ads, SEO, social media, etc.
- Interest: Engaging potential customers with content, offers, and testimonials.
- Consideration: Providing comparisons, reviews, and detailed product information.
- Conversion: The actual purchase made by the customer.
- Retention: Keeping customers engaged for repeat purchases.
Understanding and implementing market communication, brand expression, the communication mix, and an effective customer acquisition process helps businesses build strong customer relationships and increase sales.
Relationship Communication
Relationship communication refers to the way businesses interact and engage with customers, stakeholders, and partners to build long-term relationships. It focuses on trust, transparency, and customer satisfaction rather than just selling a product.
Key Aspects of Relationship Communication
- Active Listening: Understanding customer needs and concerns.
- Personalization: Offering customized solutions based on customer preferences.
- Consistent Engagement: Using emails, social media, and direct communication to maintain relationships.
- Trust and Transparency: Being honest about products, pricing, and policies.
- Feedback and Improvement: Taking customer feedback seriously and making necessary changes.
Example: Amazon excels in relationship communication by offering personalized recommendations, excellent customer service, and easy return policies, which enhance trust and customer loyalty.
Sales Responsibilities
Sales responsibilities refer to the duties of a salesperson or sales team in driving revenue, maintaining customer relationships, and achieving business targets.
Key Responsibilities of a Salesperson
- Prospecting: Identifying and reaching out to potential customers.
- Lead Qualification: Assessing whether a prospect is a good fit for the product.
- Product Presentation & Demonstration: Explaining product features and benefits.
- Negotiation & Closing Sales: Handling objections and finalizing deals.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Maintaining records of interactions and following up.
- After-Sales Support: Ensuring customer satisfaction and encouraging repeat purchases.
Example: A real estate agent has sales responsibilities like identifying potential buyers, explaining property features, negotiating prices, and providing after-sales support, ensuring a smooth home-buying experience for the customer.
While relationship communication focuses on building long-term trust with customers, sales responsibilities are about achieving revenue goals while maintaining customer satisfaction. A strong combination of both helps businesses grow and retain loyal customers.
Relationship Communication Process
The relationship communication process involves building and maintaining strong connections with customers by using clear, effective, and consistent communication. It helps in developing trust, loyalty, and long-term business relationships.
Steps in the Relationship Communication Process
Example: Nike engages with its customers through social media interactions, personalized product recommendations, and loyalty programs like Nike Membership, strengthening customer relationships.
Call Preparation
Steps in Call Preparation
Example: A SaaS (Software as a Service) company rep prepares for a sales call by researching the prospect’s company, noting how their software can solve specific issues, and planning responses to common objections before making the call.
Selling to Low-Priority and High-Priority Customers
Selling to Low-Priority Customers
Strategy:
- Use automated emails or marketing campaigns instead of personalized interactions.
- Provide self-service options like FAQs, chatbots, and recorded demos.
- Offer low-cost incentives to encourage purchases.
- Maintain periodic follow-ups without heavy investment in personal engagement.
Example: An online bookstore sends automated discount offers to inactive customers to re-engage them without spending too much on direct sales efforts.
Selling to High-Priority Customers
Strategy
- Assign dedicated account managers or sales reps.
- Offer personalized solutions based on their specific needs.
- Provide priority support and exclusive offers.
- Use relationship selling by focusing on trust-building and long-term benefits.
- Arrange in-person meetings or VIP events for premium customers.
Conclusion
- Relationship Communication builds trust and loyalty.
- Call Preparation ensures a well-structured and goal-oriented approach.
- Selling to Low-Priority Customers should be efficient and cost-effective.
- Selling to High-Priority Customers requires personalization, premium service, and relationship management.
Value Selling
Key Principles of Value Selling:
- Understand Customer Needs: Identify pain points and challenges.
- Highlight Benefits, Not Just Features: Explain how the product will add value.
- Differentiate from Competitors: Show why your solution is better.
- Demonstrate ROI (Return on Investment): Use data or testimonials to prove effectiveness.
- Create Urgency: Explain why the customer should act now.
Consequences of Poor Sales or Service
Poor sales strategies or bad customer service can lead to:
- Lost Revenue: Customers choose competitors.
- Negative Reputation: Bad reviews harm future sales.
- Low Customer Retention: Customers don’t return.
- Reduced Market Share: Competitors take over.
Order Fulfillment
Steps in Order Fulfillment
- Order Received: The business gets the customer’s order.
- Processing: The product is located and prepared for shipment.
- Packing: Items are securely packed.
- Shipping: The product is sent via delivery
Consequences of Order Fulfillment
Positive Consequences of Efficient Order Fulfillment
Negative Consequences of Poor Order Fulfillment
Example: Flipkart ensures smooth order fulfillment by integrating warehouses, delivery partners, and AI-driven inventory management to meet customer expectations.
Relationship Building in Sales
Key Strategies for Relationship Building
Example: Tesla builds strong relationships with customers by offering software updates, engaging with users through social media, and providing premium after-sales support, leading to a loyal customer base.
Conclusion
- Value Selling focuses on benefits rather than features.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment leads to customer satisfaction and business growth, while inefficiency harms reputation.
- Relationship Building ensures long-term customer engagement and repeat business.
Marketing Distribution
Distinctive Nature of Marketing Distribution
Distinctive Features of Marketing Distribution
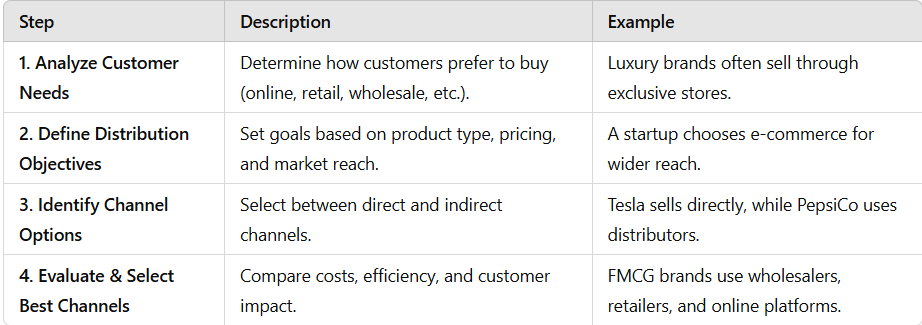
Channel Design
Steps in Channel Design
Example: Nike sells through its own stores (direct) and through retailers like Flipkart & Amazon (indirect), ensuring a broad reach.
Managing and Administering Channel Members
Key Aspects of Channel Management
Example: Amazon manages its third-party sellers by offering seller support, advertising tools, and data analytics to improve sales performance.
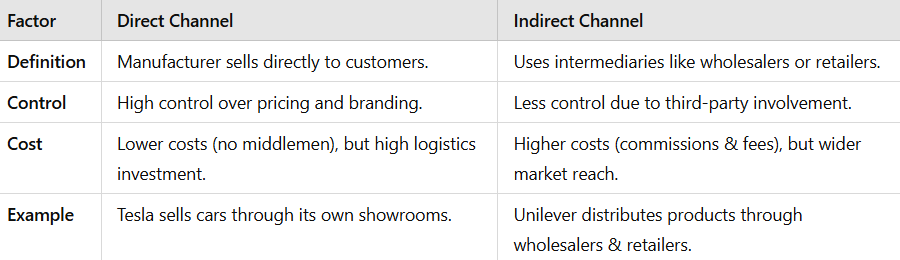
Direct & Indirect Channels
Comparison Between Direct & Indirect Channels
Example:
- Direct Channel: Apple sells iPhones via its website and official stores.
- Indirect Channel: PepsiCo sells beverages through supermarkets and wholesalers.
Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Key Elements of Supply Chain & Logistics
Example: Zara optimizes supply chain efficiency by producing fashion trends quickly and delivering them to stores within weeks, keeping inventory fresh and reducing waste.
Conclusion
- Marketing distribution ensures product availability and customer convenience.
- Channel design involves selecting the right distribution pathway.
- Managing channel members helps maintain smooth operations.
- Direct vs. Indirect channels depend on business goals and cost considerations.
- Supply chain & logistics ensure efficient product movement and customer satisfaction